Vagrant is a Configuration management tool. In this tutorial, I will use Vagrant to create an Ansible practice environment. Quickstart Vagrant create ansible your environment developer.
Table of Contents
Vagrant create ansible
Install the plugin for Vagrant
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-hosts
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-host-shell
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-vbguest
$ vagrant plugin list- vagrant-hosts: Enable name resolution between guests
- vagrant-host-shell: Make the host’s shell command executable in Vagrantfile
- vagrant-vbguest: For shared folder (automatic installation of VirtualBox Guest Additions on the guest)
Working folder for Ansible
$ mkdir -p vagrant-ansible/ansible
$ cd vagrant-ansible
$ vagrant init -m centos/7Note: I will use vagrant init -m to create a simple Vagrantfile
Vagrantfile
I will create an Ansible controller and servers.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define :ansible_controller do |ansible_controller|
ansible_controller.vm.box = "centos/7"
ENV["LC_ALL"] = "en_US.UTF-8"
config.ssh.insert_key = false
ansible_controller.vm.synced_folder "./ansible", "/home/vagrant/ansible", type: "rsync"
ansible_controller.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.3.10", :netmask => "255.255.255.0"
ansible_controller.vm.provision :hosts, :sync_hosts => true
ansible_controller.vm.provision :host_shell do |host_shell|
host_shell.inline = 'scp -i ~/.vagrant.d/insecure_private_key -o "StrictHostKeyChecking no" ~/.vagrant.d/insecure_private_key vagrant@192.168.3.10:/home/vagrant/.ssh/id_rsa'
end
ansible_controller.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
chmod 600 /home/vagrant/.ssh/id_rsa
timedatectl set-timezone asia/ho_chi_minh
yum install -y epel-release
yum -y update
yum -y install python36 python36-libs python36-devel
python36 -m ensurepip
/usr/bin/pip3 install --upgrade pip
/usr/bin/pip3 install ansible
SHELL
end
N=2
(1..N).each do |i|
config.vm.define "server#{i}" do |server|
server.vm.box = "centos/7"
config.ssh.insert_key = false
server.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.3.#{i}", :netmask => "255.255.255.0"
server.vm.provision :hosts, :sync_hosts => true
end
end
endStart vagrant
$ vagrant up
$ vagrant ssh ansible_controller
$ vagrant ssh server1
$ vagrant ssh server2The output terminal ansible install in ansible_controller as below
$ vagrant ssh ansible_controller
Last login: Thu Apr 18 14:27:27 2019 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@ansible_controller ~]$ ansible --version
ansible 2.7.10
config file = None
configured module search path = ['/home/vagrant/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/local/bin/ansible
python version = 3.6.6 (default, Mar 29 2019, 00:03:27) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)]
[vagrant@ansible_controller ~]$
Initial setting of Ansible
Create a file ansible.cfg in the folder ansible as in the example below
$ cat ./ansible/ansible.cfgThe content as below
[defaults]
inventory = ./hosts
forks = 15
log_path=$HOME/ansible/ansible.log
host_key_chcking = False
gathering = smartCreate file hosts inventory as below
$ cat ./ansible/hostsThe content hosts file as below
[servers]
server1
server2Try running Ansible
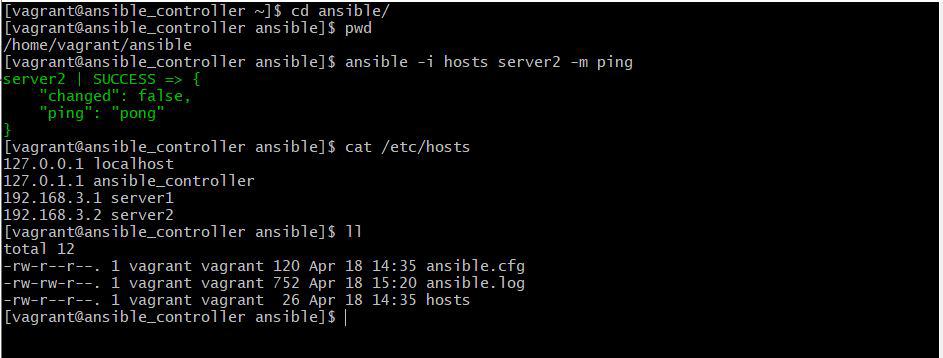
$ vagrant ssh ansible_controller
[vagrant@ansible_controller ~]$ ansible -i ansible/hosts server1 -m ping
[vagrant@ansible_controller ~]$ ansible -i ansible/hosts server2 -m pingAs the picture below
Conclusion
You have to use Vagrant create ansible. I hope will this your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!


3 thoughts on “Vagrant create ansible”