Table of Contents
Introduction
Here’s a Docker Swarm cheat sheet to help you with common commands and operations:
Docker Swarm is a powerful tool for container management and application orchestration. For those working in the DevOps field, mastering Docker Swarm commands and techniques is essential for effective system deployment and management.
This article provides a detailed cheat sheet, compiling important commands and useful tips, to help you quickly master Docker Swarm and optimize your workflow.
The Docker swarm cheat sheet
Docker swarm Management
Set up master
docker swarm init --advertise-addr <ip>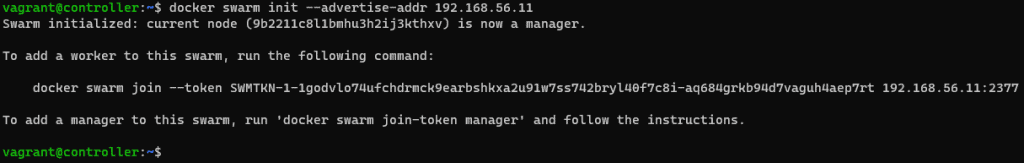
How to Force the Manager on a Broken Cluster
docker swarm init --force-new-cluster -advertise-addr <ip>Enable auto-lock
docker swarm init –autolockGet a token to join the workers
docker swarm join-token worker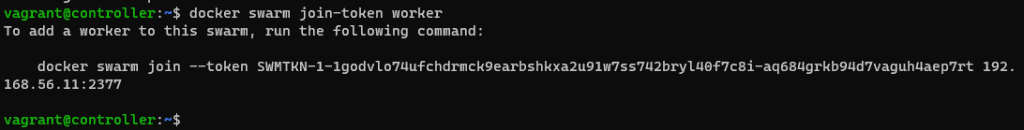
Get a token to join the new manager
docker swarm join-token manager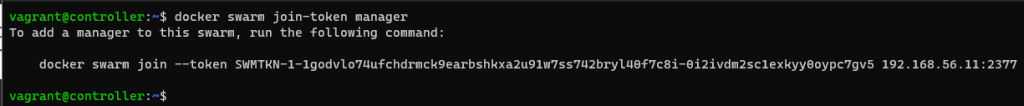
Join the host as a worker
docker swarm join <server> workerHave a node leave a swarm
docker swarm leaveUnlock a manager host after the docker
docker swarm unlockPrint key needed for ‘unlock’
docker swarm unlock-keyPrint swarm node list
docker node ls
Docker Service Management
Create a new service:
docker service create <options> <image> <command>List the services running in a swarm
docker service lsInspect a service:
docker service inspect <service-id>Scale a service (increase or decrease replicas)
docker service scale <service-id>=<replica-count>Update a service:
docker service update <options> <service-id>Remove a service:
docker service rm <service-id>List the tasks of the service_name
docker service ps service_namelist running (active) tasks for a given service
docker service ps --filter desired-state=running <service id|name>print console log of a service
docker service logs --follow <service id|name>Promote a worker node to the manager
docker node promote node_nameThe output terminal Promote a worker node to the manager as below
vagrant@controller:~$ docker node ls
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION
9b2211c8l1bmhu3h2ij3kthxv * controller Ready Active Leader 20.10.14
0j0pslqf4g6xkki8ajydvc123 node1 Ready Active 20.10.14
f4cxubqg0wqdxsaj8pe4qsqlg node2 Ready Active 20.10.14
vagrant@controller:~$ docker node promote f4cxubqg0wqdxsaj8pe4qsqlg
Node f4cxubqg0wqdxsaj8pe4qsqlg promoted to a manager in the swarm.
vagrant@controller:~$ docker node ls
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION
9b2211c8l1bmhu3h2ij3kthxv * controller Ready Active Leader 20.10.14
0j0pslqf4g6xkki8ajydvc123 node1 Ready Active 20.10.14
f4cxubqg0wqdxsaj8pe4qsqlg node2 Ready Active Reachable 20.10.14Docker Stack Management
List running swarms
docker stack lsDeploy a stack using a Compose file:
docker stack deploy --compose-file <compose-file> <stack-name>Inspect a stack:
docker stack inspect <stack-name>List services in a stack:
docker stack services <stack-name>List containers in a stack:
docker stack ps <stack-name>Remove a stack:
docker stack rm <stack-name>Conclusion
You now have the Docker Swarm cheat sheet, which includes some of the most essential commands used in Docker Swarm.
For a more comprehensive list of options and additional commands, please refer to the official Docker documentation:
For a more detailed list of options and additional commands, you can refer to the official Docker documentation. I hope you find this helpful. Thank you for visiting the DevopsRoles page!

