Table of Contents
Introduction
In this tutorial, How to ansible testinfra test infrastructure. You can write unit tests in Python to test the actual status of your target servers.
Ansible Testinfra is a testing framework that allows you to write tests for your Ansible playbooks and roles. It is built on top of the popular Python testing framework pytest and provides a simple way to test the state of your systems after running Ansible playbooks.
Testinfra is a powerful library for writing tests to verify an infrastructure’s state. It is a Python library and uses the powerful pytest test engine.
Ansible Testinfra test infrastructure
Install Testinfra
Method 1: Use pip ( Python package manager ) to install Testinfra and a Python virtual environment.
python3 -m venv ansible
source ansible/bin/activate
(ansible) $ pip install testinfra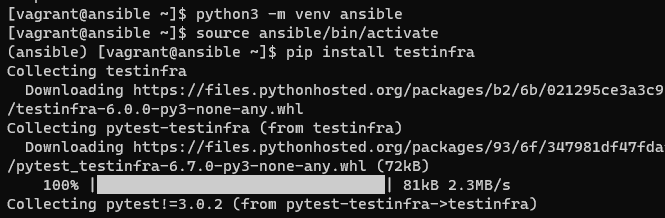
Method 2: Testinfra is also available in the package repositories of Fedora and CentOS using the EPEL repository. For example, install on CentOS 7 as command below:
$ yum install -y epel-release
$ yum install -y python-testinfraFor example, A simple test script
I create test.py with the content below:
import testinfra
def test_os_release(host):
assert host.file("/etc/os-release").contains("centos")
def test_sshd_active(host):
assert host.service("sshd").is_running is TrueTo run these tests on your local machine, execute the following command:
(ansible)$ pytest test.py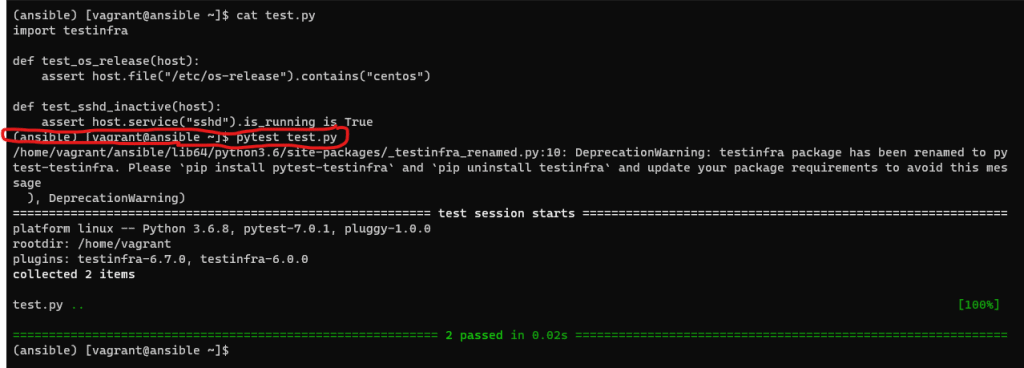
Testinfra and Ansible
Use pip to install the Ansible package.
pip install ansibleHere is the resulting output:
(ansible) [vagrant@ansible ~]$ pip install ansible
Collecting ansible
Downloading ansible-4.10.0.tar.gz (36.8 MB)
|████████████████████████████████| 36.8 MB 6.9 MB/s
Preparing metadata (setup.py) ... done
Collecting ansible-core~=2.11.7
Downloading ansible-core-2.11.11.tar.gz (7.1 MB)
|████████████████████████████████| 7.1 MB 9.6 MB/s
Preparing metadata (setup.py) ... done
Collecting jinja2
Downloading Jinja2-3.0.3-py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 133 kB 10.4 MB/s
Collecting PyYAML
Downloading PyYAML-6.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux_2_5_x86_64.manylinux1_x86_64.manylinux_2_12_x86_64.manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (603 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 603 kB 8.7 MB/s
Collecting cryptography
Downloading cryptography-37.0.2-cp36-abi3-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (4.1 MB)
|████████████████████████████████| 4.1 MB 11.5 MB/s
Requirement already satisfied: packaging in ./ansible/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from ansible-core~=2.11.7->ansible) (21.3)
Collecting resolvelib<0.6.0,>=0.5.3
Downloading resolvelib-0.5.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (12 kB)
Collecting cffi>=1.12
Downloading cffi-1.15.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux_2_5_x86_64.manylinux1_x86_64.whl (405 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 405 kB 10.7 MB/s
Collecting MarkupSafe>=2.0
Downloading MarkupSafe-2.0.1-cp36-cp36m-manylinux_2_5_x86_64.manylinux1_x86_64.manylinux_2_12_x86_64.manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (30 kB)
Requirement already satisfied: pyparsing!=3.0.5,>=2.0.2 in ./ansible/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from packaging->ansible-core~=2.11.7->ansible) (3.0.9)
Collecting pycparser
Downloading pycparser-2.21-py2.py3-none-any.whl (118 kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 118 kB 12.3 MB/s
Using legacy 'setup.py install' for ansible, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Using legacy 'setup.py install' for ansible-core, since package 'wheel' is not installed.
Installing collected packages: pycparser, MarkupSafe, cffi, resolvelib, PyYAML, jinja2, cryptography, ansible-core, ansible
Running setup.py install for ansible-core ... done
Running setup.py install for ansible ... done
Successfully installed MarkupSafe-2.0.1 PyYAML-6.0 ansible-4.10.0 ansible-core-2.11.11 cffi-1.15.0 cryptography-37.0.2 jinja2-3.0.3 pycparser-2.21 resolvelib-0.5.4
(ansible) [vagrant@ansible ~]$Testinfra can directly use Ansible’s inventory file and a group of machines defined in the inventory. For example, inventory hosts are the target server Ubuntu.
(ansible) [vagrant@ansible ~]$ cat hosts
[target-server]
UbuntuServerWe verify the operating system and ensure that SSH is running on the target server.
To test using Testinfra and Ansible, use the following command:
pytest -vv --sudo --hosts=target-server --ansible-inventory=hosts --connection=ansible test.pyThe terminal output is as follows:
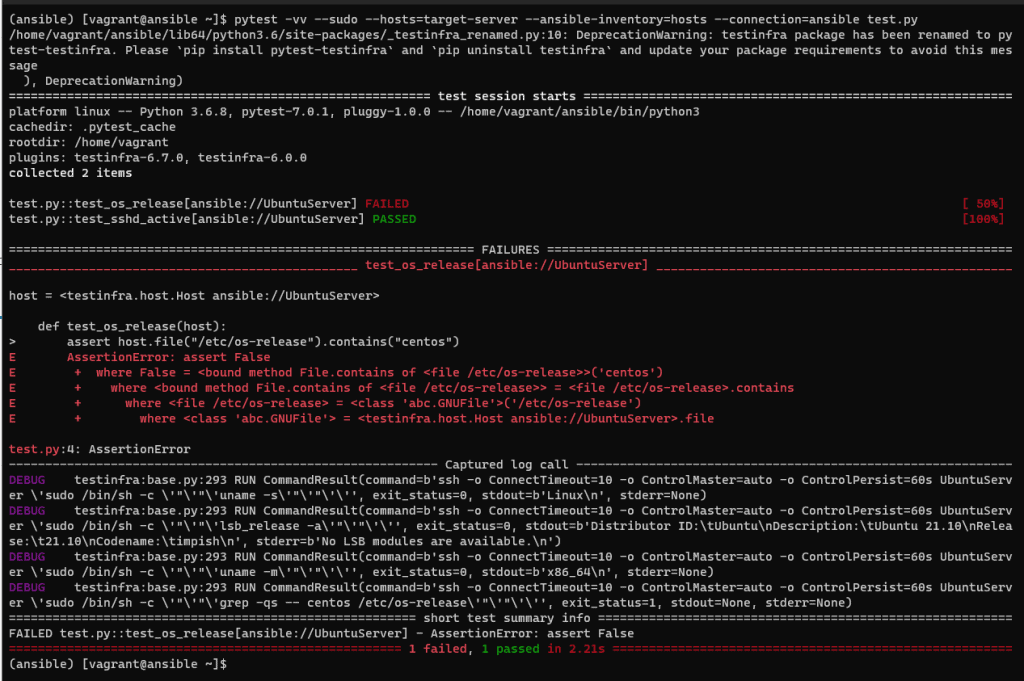
Conclusion
You have Ansible Testinfra test infrastructure. Ansible and Testinfra are complementary tools that can be used together in an infrastructure provisioning and testing workflow, but they serve different purposes.
Ansible specializes in automation and configuration management, whereas Testinfra is dedicated to testing the infrastructure. I hope you find this information helpful. Thank you for visiting the DevopsRoles page!
