Table of Contents
Introduction
In this tutorial, you will create a Lambda to access ElastiCache cluster. When you create the Lambda function, you provide subnet IDs in your Amazon VPC and a VPC security group to allow the Lambda function to access resources in your VPC. For illustration in this tutorial, the Lambda function generates a UUID, writes it to the cache, and retrieves it from the cache.
Invoke the Lambda function and verify that it accessed the ElastiCache cluster in your VPC.
Prerequisites
Before starting, you should have the following prerequisites configured
- An AWS account
- AWS CLI on your computer
- A Memcached cluster (refer Memcached tutorial to create a Memcached cluster )
Create a Lambda to access ElastiCache in an Amazon VPC
- Create the execution role
- Create an ElastiCache cluster
- Create a deployment package
- Create the Lambda function
- Test the Lambda function
- Clean up
Create the execution role
Create the execution role that gives your function permission to access AWS resources. To create an execution role with the AWS CLI, use the create-role command.
In the following example, you specify the trust policy inline.
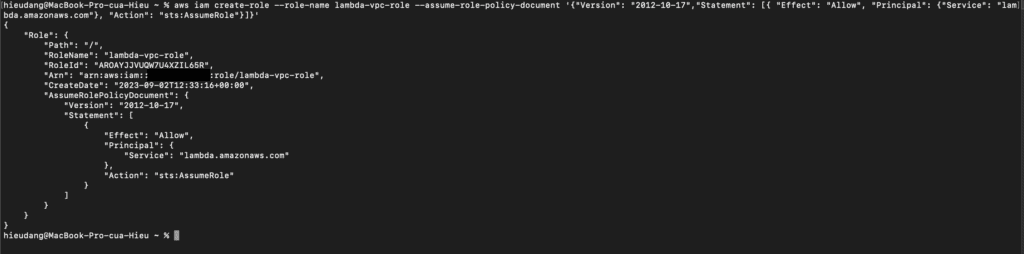
aws iam create-role --role-name lambda-vpc-role --assume-role-policy-document '{"Version": "2012-10-17","Statement": [{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": {"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"}, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole"}]}'You can also define the trust policy for the role using a JSON file. In the following example, trust-policy.json is a file in the current directory. Example trust-policy.json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Add permissions to the role, and use the attach-policy-to-role command. Start by adding the AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole managed policy.
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name lambda-vpc-role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole
Create an ElastiCache cluster
Refer Memcached tutorial to create a Memcached cluster.
The following command retrieves the configuration endpoint (ConfigurationEndpoint)
aws elasticache describe-cache-clusters \
--cache-cluster-id my-cluster --query 'CacheClusters[].ConfigurationEndpoint'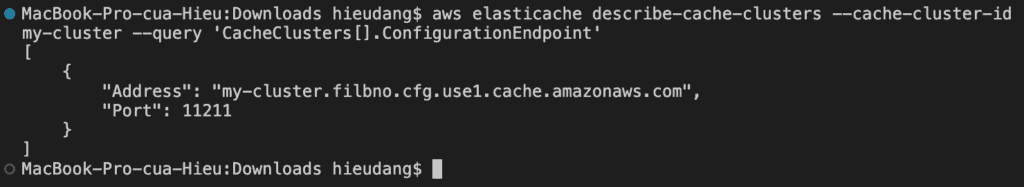
Create a deployment package
In the following example, create app.py a file in the current directory. Example app.py
from __future__ import print_function
import time
import uuid
import sys
import socket
import elasticache_auto_discovery
from pymemcache.client.hash import HashClient
#elasticache settings
elasticache_config_endpoint = "your-elasticache-cluster-endpoint:port"
nodes = elasticache_auto_discovery.discover(elasticache_config_endpoint)
nodes = map(lambda x: (x[1], int(x[2])), nodes)
memcache_client = HashClient(nodes)
def handler(event, context):
"""
This function puts into memcache and get from it.
Memcache is hosted using elasticache
"""
#Create a random UUID... this will be the sample element we add to the cache.
uuid_inserted = uuid.uuid4().hex
#Put the UUID to the cache.
memcache_client.set('uuid', uuid_inserted)
#Get item (UUID) from the cache.
uuid_obtained = memcache_client.get('uuid')
if uuid_obtained.decode("utf-8") == uuid_inserted:
# this print should go to the CloudWatch Logs and Lambda console.
print ("Success: Fetched value %s from memcache" %(uuid_inserted))
else:
raise Exception("Value is not the same as we put :(. Expected %s got %s" %(uuid_inserted, uuid_obtained))
return "Fetched value from memcache: " + uuid_obtained.decode("utf-8")Dependencies
- elasticache-auto-discovery – The Lambda function uses this library to get the nodes in your Amazon ElastiCache cluster.
- pymemcache – The Lambda function code uses this library to create an
HashClientobject to set and get items from memcache.
Create a deployment package.
zip -r function.zip app.py pymemcache/* elasticache_auto_discovery/*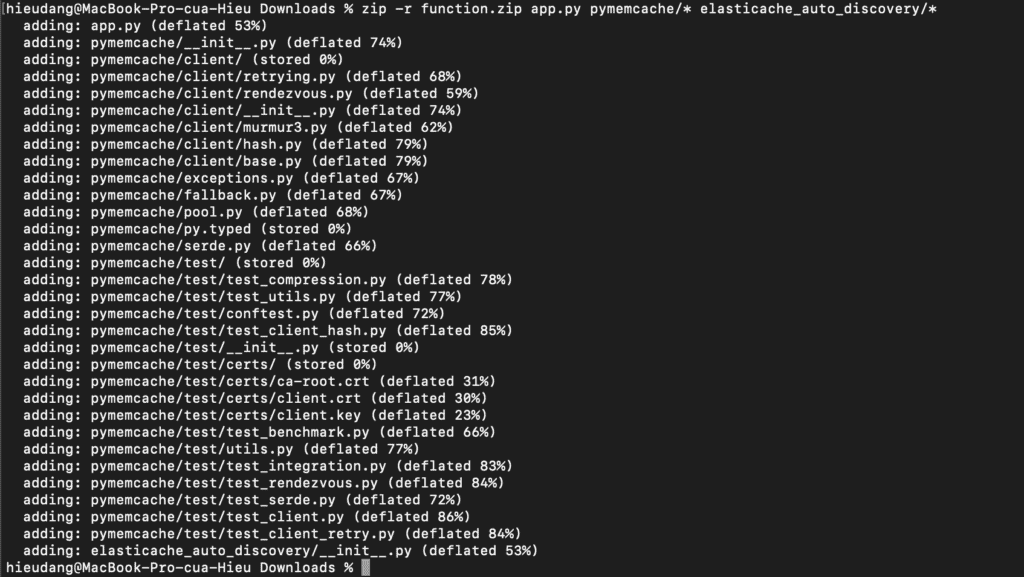
Create the Lambda function
Create the Lambda function with the create-function command.
aws lambda create-function --function-name AccessMemCache --timeout 30 --memory-size 1024 \
--zip-file fileb://function.zip --handler app.handler --runtime python3.8 \
--role arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/lambda-vpc-role \
--vpc-config SubnetIds=subnet-0a8aaace20a7efd26,subnet-0daa531c4e748062d,subnet-0de820fd0f0efded5,SecurityGroupIds=sg-083f2ca0560111a3b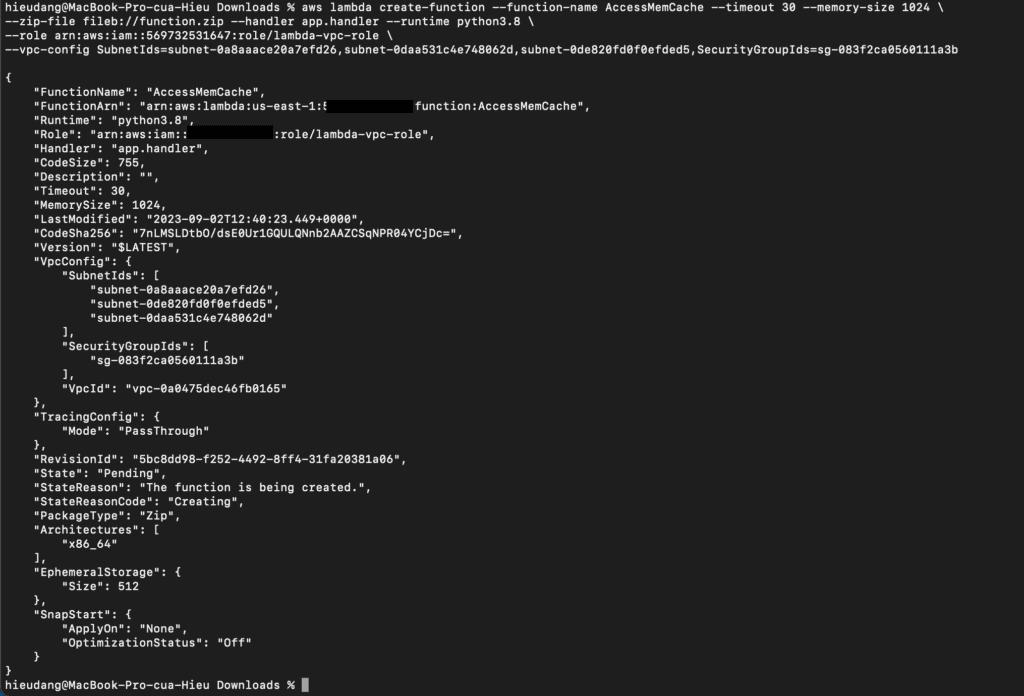
Test the Lambda function
In this step, you invoke the Lambda function manually using the invoke command. When the Lambda function runs, it generates a UUID and writes it to the ElastiCache cluster specified in your Lambda code. The Lambda function then retrieves the item from the cache.
Invoke the Lambda function with the invoke the command includes getting log stream from CloudWatch
aws lambda invoke --function-name AccessMemCache --cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out --payload '{"key": "value"}' out
Clean up
Run the following delete-function command to delete the AccessMemCache function.
aws lambda delete-function --function-name AccessMemCacheRun the following command to delete an IAM role
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name lambda-vpc-role
aws iam detach-role-policy --role-name lambda-vpc-role --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaVPCAccessExecutionRole
aws iam delete-role --role-name lambda-vpc-role
Conclusion
These steps provide an example to manage the Memcached cluster. The specific configuration details may vary depending on your environment and setup. It’s recommended to consult the relevant documentation from AWS for detailed instructions on setting up. I hope this will your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!
Refer


