Table of Contents
Introduction
In this tutorial, How to use Docker setup Nginx Flask and Postgres.
Prerequisites
- Install Docker
- (optional) Install docker-compose
Docker setup Nginx Flask and Postgres
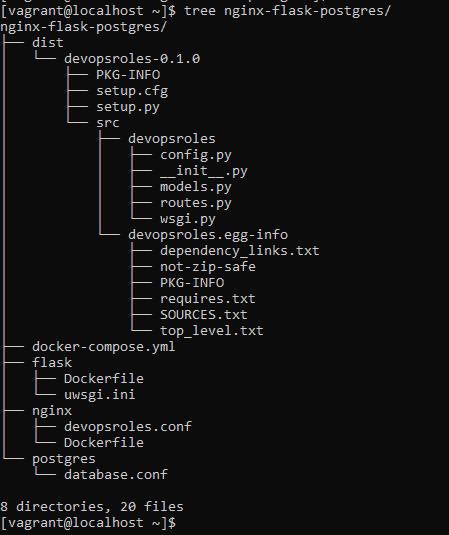
The structure folder and file of the app.
Nginx
The first Docker Nginx. It will be used as a proxy server.
User --> Nginx --> Python applicationDockerfile file
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ cat nginx/Dockerfile
FROM nginx:latest
RUN rm /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
COPY nginx/devopsroles.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/Example devopsroles.conf file
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
try_files $uri @app;
}
location @app {
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass flask:8080;
}
}Flask
The second Docker container Python application running on a uWSGI server.
Dockerfile file
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ cat nginx/Dockerfile
FROM nginx:latest
RUN rm /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
COPY nginx/devopsroles.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ cat flask/Dockerfile
# Base Image
FROM python:3.6-alpine as BASE
RUN apk add --no-cache linux-headers g++ postgresql-dev gcc build-base linux-headers ca-certificates python3-dev libffi-dev libressl-dev libxslt-dev
RUN pip wheel --wheel-dir=/root/wheels psycopg2
RUN pip wheel --wheel-dir=/root/wheels cryptography
# Actual Image
FROM python:3.6-alpine as RELEASE
EXPOSE 8080
WORKDIR /app
ENV POSTGRES_USER="" POSTGRES_PASSWORD="" POSTGRES_HOST=postgres POSTGRES_PORT=5432 POSTGRES_DB=""
COPY dist/ ./dist/
COPY flask/uwsgi.ini ./
COPY --from=BASE /root/wheels /root/wheels
RUN apk add --no-cache build-base linux-headers postgresql-dev pcre-dev libpq uwsgi-python3 && \
pip install --no-index --find-links=/root/wheels /root/wheels/* && \
pip install dist/*
CMD ["uwsgi", "--ini", "/app/uwsgi.ini"]Note:
- It exposes port 8080
- creates a default directory /app/
uwsgi.ini file
[uwsgi]
socket = :8080
module = devopsroles.wsgi:app
master = 1
processes = 4
plugin = pythonPostgres
Get Postgres the latest Postgres image from Docker Hub. Then we pass environment variables to it.
Example: database.conf file
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ cat postgres/database.conf
POSTGRES_USER=test
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
POSTGRES_HOST=postgres
POSTGRES_PORT=5432
POSTGRES_DB=devopsrolesThe final docker-compose.yml
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ pwd
/home/vagrant/nginx-flask-postgres
[vagrant@localhost nginx-flask-postgres]$ cat docker-compose.yml
version: '3.5'
services:
web_server:
container_name: nginx
build:
context: .
dockerfile: nginx/Dockerfile
ports:
- 80:80
depends_on:
- app
app:
container_name: flask
build:
context: .
dockerfile: flask/Dockerfile
env_file: postgres/database.conf
expose:
- 8080
depends_on:
- database
database:
container_name: postgres
image: postgres:latest
env_file: postgres/database.conf
ports:
- 5432:5432
volumes:
- db_volume:/var/lib/postgresql
volumes:
db_volume:Docker Compose Build and Run
docker-compose up --build -dThe result Docker container Nginx, Flask, and Postgres

Conclusion
You have Deploy Docker setup Nginx Flask and Postgres. I hope will this your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!


