Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Prerequisites
- 3 Memcached tutorial
- 3.1 Creating a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.2 Modifying a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.3 Viewing the elements in a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.4 Discovering the endpoints of Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.5 Adding nodes to a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.6 Removing nodes from a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- 3.7 Auto Scaling ElastiCache for Redis clusters
- 3.7.1 Prerequisites
- 3.7.2 ElastiCache for Redis supports scaling for the following dimensions:
- 3.7.3 ElastiCache for Redis supports the following types of automatic scaling policies:
- 3.7.4 Using Auto Scaling with shards
- 3.7.5 Deleting a scaling policy using the AWS CLI
- 3.7.6 Using Auto Scaling with replicas
- 3.7.7 Deleting a scaling policy using the AWS CLI
- 3.8 Redis clusters manual failover with Global datastore
- 4 Conclusion
Introduction
In this tutorial on Memcached, you will learn how to create an ElastiCache for Redis instance and manage it using the AWS CLI.
Prerequisites
Before starting, you should have the following prerequisites configured
- An AWS account
- AWS CLI on your computer
Memcached tutorial
- Creating a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Modifying a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Viewing the elements in a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Discovering the endpoints of Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Adding nodes to a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Removing nodes from a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
- Auto Scaling ElastiCache for Redis clusters
- Redis clusters manual failover with Global datastore
- Deleting a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
Creating a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
Before you begin, If you have not installed the AWS CLI, see Setting up the Amazon Redshift CLI. This tutorial uses the us-ease-1 region.
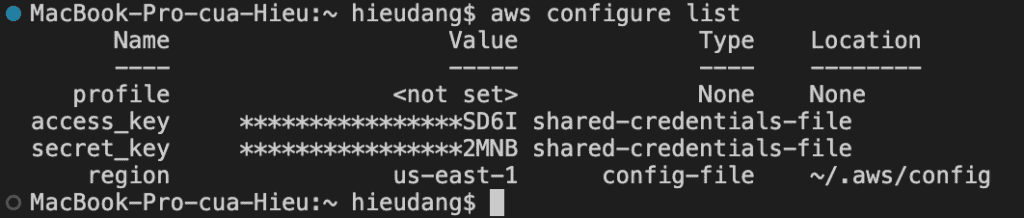
Now we’re ready to launch a Redis cluster by using the AWS CLI.
Typical cluster configurations:
- Redis (cluster mode enabled): can have up to 500 shards, with your data partitioned across the shards.
- Redis (cluster mode disabled):always contain just one shard (in the API and CLI, one node group). A Redis shard contains one to six nodes. If there is more than one node in a shard, the shard supports replication. In this case, one node is the read/write primary node and the others are read-only replica nodes.
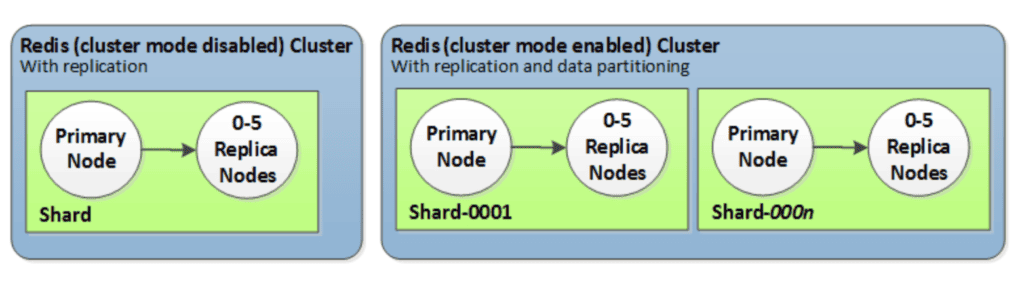
In this tutorial we will create a Redis (cluster mode enabled) using AWS CLI.
Before you create a cluster, you first create a subnet group. A cache subnet group is a collection of subnets that you may want to designate for your cache clusters in a VPC.
aws elasticache create-cache-subnet-group \
--cache-subnet-group-name my-subnetgroup \
--cache-subnet-group-description "Testing" \
--subnet-ids "subnet-0a8aaace20a7efd26" "subnet-0daa531c4e748062d" "subnet-0de820fd0f0efded5"The following procedure creates a Redis (cluster mode enabled) replication group using the AWS CLI.
#create
aws elasticache create-replication-group \
--replication-group-id cluster-primary \
--replication-group-description "Demo cluster with replicas" \
--num-node-groups 2 \
--replicas-per-node-group 1 \
--cache-node-type cache.m4.large \
--engine redis \
--security-group-ids sg-083f2ca0560111a3b \
--automatic-failover-enabled \
--multi-az-enabled \
--cache-subnet-group-name my-subnetgroup
#check status
aws elasticache describe-replication-groups \
--replication-group-id cluster-primary \
--region us-east-1 |\
jq -r .ReplicationGroups[0].Status
This command returns the following result.
Modifying a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
You can modify an existing cluster using the AWS CLI modify-cache-cluster operation. To modify a cluster’s configuration value, specify the cluster’s ID, the parameter to change and the parameter’s new value. Refer Memcached tutorial to know this command.
Viewing the elements in a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
The following command to view details for my-cluster:
aws elasticache describe-replication-groups --replication-group-id my-cluster This command returns the following result.
Discovering the endpoints of Redis cluster with AWS CLI
You can use the AWS CLI to discover the endpoints for a replication group and its clusters with the describe-replication-groups command. The command returns the replication group’s primary endpoint and a list of all the clusters (nodes) in the replication group with their endpoints, along with the reader endpoint.
aws elasticache describe-replication-groups \
--replication-group-id myreplgroupThis command returns the following result.
Adding nodes to a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
You can online resharding with Regis cluster (there is some degradation in performance, nevertheless, your cluster continues to serve requests throughout the scaling operation). When you add shards to a Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster, any tags on the existing shards are copied over to the new shards.
There are two ways to scale your Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster; horizontal and vertical scaling.
- Horizontal scaling allows you to change the number of node groups (shards) in the replication group by adding or removing node groups (shards). The online resharding process allows scaling in/out while the cluster continues serving incoming requests. Configure the slots in your new cluster differently than they were in the old cluster. Offline method only.
- Vertical Scaling – Change the node type to resize the cluster. The online vertical scaling allows scaling up/down while the cluster continues serving incoming requests.
The following process describes how to reconfigure the shards in your Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster by adding shards using the AWS CLI.
aws elasticache modify-replication-group-shard-configuration \
--replication-group-id my-cluster \
--node-group-count 4 \
--resharding-configuration \
"PreferredAvailabilityZones=us-east-2a,us-east-2c" \
"PreferredAvailabilityZones=us-east-2b,us-east-2a" \
"PreferredAvailabilityZones=us-east-2c,us-east-2d" \
"PreferredAvailabilityZones=us-east-2d,us-east-2c" \
--apply-immediatelyThis command returns the following result.
Removing nodes from a Redis cluster with AWS CLI
The following process describes how to reconfigure the shards in your Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster by removing shards using the AWS CLI.
aws elasticache modify-replication-group-shard-configuration \
–replication-group-id my-cluster \
–node-group-count 2 \
–node-groups-to-remove “0002” “0003” \
–apply-immediately
This command returns the following result.
Auto Scaling ElastiCache for Redis clusters
Prerequisites
ElastiCache for Redis Auto Scaling is limited to the following:
- Redis (cluster mode enabled) clusters running Redis engine version 6.0 onwards
- Data tiering (cluster mode enabled) clusters running Redis engine version 7.0.7 onwards
- Instance type families – R7g, R6g, R5, M7g, M6g, M5
- Instance sizes – Large, XLarge, 2XLarge
- Auto Scaling in ElastiCache for Redis is not supported for clusters running in Global datastores, Outposts or Local Zones.
- AWS Auto Scaling for ElastiCache for Redis is not available in the following regions: China (Beijing), China (Ningxia), AWS GovCloud (US-West) and AWS GovCloud (US-East).
ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling is the ability to increase or decrease the desired shards or replicas in your ElastiCache for Redis service automatically. ElastiCache for Redis leverages the Application Auto Scaling service to provide this functionality. For more information, see Application Auto Scaling. To use automatic scaling, you define and apply a scaling policy that uses CloudWatch metrics and target values that you assign. ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling uses the policy to increase or decrease the number of instances in response to actual workloads.
ElastiCache for Redis supports scaling for the following dimensions:
- Shards – Automatically add/remove shards in the cluster similar to manual online resharding. In this case, ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling triggers scaling on your behalf.
- Replicas – Automatically add/remove replicas in the cluster similar to manual Increase/Decrease replica operations. ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling adds/removes replicas uniformly across all shards in the cluster.
ElastiCache for Redis supports the following types of automatic scaling policies:
- Target tracking scaling policies – Increase or decrease the number of shards/replicas that your service runs based on a target value for a specific metric. This is similar to the way that your thermostat maintains the temperature of your home. You select a temperature and the thermostat does the rest.
- Scheduled scaling for Application ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling – Increase or decrease the number of shards/replicas that your service runs based on the date and time.
Using Auto Scaling with shards
Defining a scaling policy
Currently, ElastiCache for Redis supports the following predefined metrics in ElastiCache for Redis NodeGroup Auto Scaling:
- ElastiCachePrimaryEngineCPUUtilization – The average value of the
EngineCPUUtilizationmetric in CloudWatch across all primary nodes in the ElastiCache for Redis cluster. - ElastiCacheDatabaseMemoryUsageCountedForEvictPercentage – The average value of the
DatabaseMemoryUsageCountedForEvictPercentagemetric in CloudWatch across all primary nodes in the ElastiCache for Redis cluster. - ElastiCacheDatabaseCapacityUsageCountedForEvictPercentage – The average value of the
ElastiCacheDatabaseCapacityUsageCountedForEvictPercentagemetric in CloudWatch across all primary nodes in the ElastiCache for Redis cluster.
The following example cpuscalablepolicy.json describes a target-tracking configuration for a scaling policy for EngineCPUUtilization metric.
{
"TargetValue": 50,
"CustomizedMetricSpecification":
{
"MetricName": "EngineCPUUtilization",
"Namespace": "AWS/ElastiCache",
"Dimensions": [
{
"Name": "RelicationGroup","Value": "my-db-cluster"
},
{
"Name": "Role","Value": "PRIMARY"
}
],
"Statistic": "Average",
"Unit": "Percent"
},
"ScaleInCooldown": 600,
"ScaleOutCooldown": 300
}In the following example, you apply a target-tracking scaling policy named cpuscalablepolicy to an ElastiCache for Redis cluster named myscalablecluster with ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling. To do so, you use a policy configuration saved in a file named cpuscalablepolicy.json.
aws application-autoscaling put-scaling-policy \
--policy-name cpuscalablepolicy \
--policy-type TargetTrackingScaling \
--resource-id replication-group/myscalablecluster \
--service-namespace elasticache \
--scalable-dimension elasticache:replication-group:NodeGroups \
--target-tracking-scaling-policy-configuration file://cpuscalablepolicy.jsonRegistering a Scalable Target
Before you can use Auto Scaling with an ElastiCache for Redis cluster, you register your cluster with ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling.
In the following example, you register an ElastiCache for Redis cluster named myscalablecluster. The registration indicates that the cluster should be dynamically scaled to have from one to ten shards.
aws application-autoscaling register-scalable-target \
--service-namespace elasticache \
--resource-id replication-group/myscalablecluster \
--scalable-dimension elasticache:replication-group:NodeGroups \
--min-capacity 1 \
--max-capacity 10 \--max-capacity– The maximum number of shards to be managed by ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling. For information about the relationship between--min-capacity,--max-capacity, and the number of shards in your cluster, see Minimum and maximum capacity.--min-capacity– The minimum number of shards to be managed by ElastiCache for Redis auto scaling. For information about the relationship between--min-capacity,--max-capacity, and the number of shards in your cluster, see Minimum and maximum capacity.
Deleting a scaling policy using the AWS CLI
In the following example, you delete a target-tracking scaling policy named myscalablepolicy from an ElastiCache for Redis cluster named myscalablecluster.
aws application-autoscaling delete-scaling-policy \
--policy-name myscalablepolicy \
--resource-id replication-group/myscalablecluster \
--service-namespace elasticache \
--scalable-dimension elasticache:replication-group:NodeGroupsUsing Auto Scaling with replicas
Defining a scaling policy
Registering a Scalable Target
Deleting a scaling policy using the AWS CLI
Redis clusters manual failover with Global datastore
Create a Global Datastore using the primary replication group.
aws elasticache create-global-replication-group \
--global-replication-group-id-suffix multi-region \
--primary-replication-group-id cluster-primary \
--region us-east-1Create new cluster in the Secondary Region and add to Global Datastore
aws elasticache create-replication-group \
--replication-group-id cluster-secondary \
--replication-group-description "DR Workshop Labs" \
--global-replication-group-id ldgnf-multi-region \
--multi-az-enabled \
--num-cache-clusters 2 \
--region us-west-1Check if both clusters are with Status “associated”
aws elasticache describe-global-replication-groups \
--global-replication-group-id ldgnf-multi-region \
--show-member-info --region us-east-1 |\
jq -r .GlobalReplicationGroups[0].Members
Promote Secondary Cluster to Primary
aws elasticache failover-global-replication-group \
–global-replication-group-id ldgnf-multi-region \
–primary-region us-west-1 \
–primary-replication-group-id cluster-secondary \
–region us-east-1
Cleaning up
Remove the cluster-primary from Global Datastore.
aws elasticache disassociate-global-replication-group \
--global-replication-group-id ldgnf-multi-region \
--replication-group-id cluster-primary \
--replication-group-region us-east-1 \
--region us-east-1Delete cluster-primary
aws elasticache delete-replication-group \
--replication-group-id cluster-primary \
--no-retain-primary-cluster \
--region us-east-1Delete Global Datastore.
aws elasticache delete-global-replication-group \
--global-replication-group-id ldgnf-multi-region \
--retain-primary-replication-group \
--region us-east-1
Delete cluster-secondary.
aws elasticache delete-replication-group \
--replication-group-id cluster-secondary \
--no-retain-primary-cluster \
--region us-west-1
Conclusion
These steps provide an example to manage Memcached cluster. The specific configuration details may vary depending on your environment and setup. It’s recommended to consult the relevant documentation from AWS for detailed instructions on setting up. I hope will this your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!
Refer
https://disaster-recovery.workshop.aws/en/labs/basics/elasticache-global-datastore.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/red-ug/Clusters.html