Table of Contents
Introduction
In this guide, We’ll explore how to use gitlab SSH keys for Git operations in your projects. Learn the step-by-step process to generate an SSH key pair for GitLab and integrate it with your account.
To effectively use GitLab via SSH, you must create an SSH key pair and link the public key with your GitLab account.
How to do Gitlab SSH key pair
Open a terminal on your Linux system.
If you do not have an SSH key pair, then the error message is as below:
$ cat ~huupv/.ssh/id_rsa.pub cat: /home/huupv/.ssh/id_rsa.pub: No such file or directory
To generate a new ssh key pair by running the following command
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "huupv@devopsroles.com" -b 4096
Replace “huupv@devopsroles.com” with your actual email address associated with your GitLab account. You can press Enter to accept the default file path and passphrase (or set a passphrase for added security).
The output Gitlab SSH key pair is below
Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/huupv/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/home/huupv/.ssh'. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/huupv/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/huupv/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 2a:16:6d:94:35:a2:02:db:2c:ce:fb:4f:79:56:bf:0b huupv@devopsroles.com The key's randomart image is: +--[ RSA 4096]----+
To generate 2 files as below:
Private key: id_rsa Public key: id_rsa.pub
I already have ssh key pair to create on my laptop.
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
The content public key id_rsa.pub is as below:
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAgEAwEts938rLe7B1KKgYYBrhCMHFzeumk1IaoVo3rD48qVCig8fCHvp+W3Z2UzHHS9iT1IscXi0Bxq+/fTO9cbB5EznGTIW3I7y26yzIq/6iv3I/biYMmi6EiWCd2Ed2188uZ9aR0+gN4QIAmU8Grh91eaEy04d9H67GF2UT3lqx3PEi7v7aIH6FdkCdOp2YIE25UTuJoMoZ3kjKo02tGP7y/PUw8lbm/ezvYFLBN5l5DfmebDwSBNrR/K84mLWGx3L/bB9XnkEZRSh2vi+YFQ5FMomJA8+RHzfUS5zV3tI8VFDe1bGvcpYxKLKGc1bfKBZSYsOpsKgOofBcENaOJ8l0xCLWMFbJkAKcLEFuwBpLTx75WF7MEaxBnEIWekhhBR5hC+cR2fKEYuZaOYmpBfZUGnIDadad83+3qOQs+50/11AoinHCBOEphWRbn6pk0JP+pyTDsRKEmZ4KNOJt/WNwfVMnCVKb/5wcwCrmQ8ztWilcjT0UdMYUoH4u2IidWV5F38vAdG+LNH5dmKr2pcI7CdgZSXQqppkrvcqMLeH2BprlxuJW8qLc1hYV6HhWYbJc3EX28a6mZfohXLQAgN8HVpBaQ9UAZ33MiDPUhHeIW1OeXSXQHgH5t0CjXqzg3G9/vM7qOUr/27kN+D0ExBPENQf7hZ5Aw24fJl/PLQHAHs= huupv@devopsroles.com
Copy and paste the content id_rsa.pub to the Profile Settings in the Gitlab server web interface. ( step by step as below)
Copy the ssh key to GitLab
Copy the contents of the public key by running the following command: cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- Copy the entire public key output from the terminal.
- Now, log in to your GitLab account using a web browser.
- In the top right corner, click on your profile picture and select “Settings.”
- From the left-hand side menu, click on “SSH Keys.”
- Paste the copied public key into the “Key” field.
- Optionally, give a recognizable “Title” to the SSH key (e.g., “My Linux Workstation”).
- Click on the “Add key” button to save the SSH key to your GitLab account.
- The SSH key is now added to your GitLab account, and you can use SSH to interact with GitLab repositories.
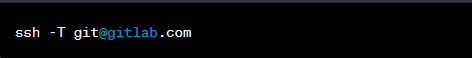
To test the SSH key connection
You can run the following command in the terminal:
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ll guide you on how to set up and use an SSH key pair for your project. You’ll learn the straightforward steps to generate an SSH key pair that secures your account. This essential setup enhances the security of your project by ensuring that only authorized users can access it. Follow along to easily create and implement your SSH keys.
You are now ready to use your GitLab SSH key for secure interactions with your repositories. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

