Table of Contents
#Introduction
In this tutorial, How to Install Kubernetes Cluster with KubeKey. I will deploy a Kubernetes Cluster using KubeKey Quickstart.
You can use KubeKey to spin up a Kubernetes deployment for development/testing purposes. As Kubernetes is the de-facto standard in container orchestration.
Requirements install Kubernetes Cluster with KubeKey
- Running instance of Ubuntu Server.
- A user with sudo privileges.
Install Docker
First, You need to install Docker on the Ubuntu server. Refer to How to install docker on Ubuntu Server.
How to Install KubeKey
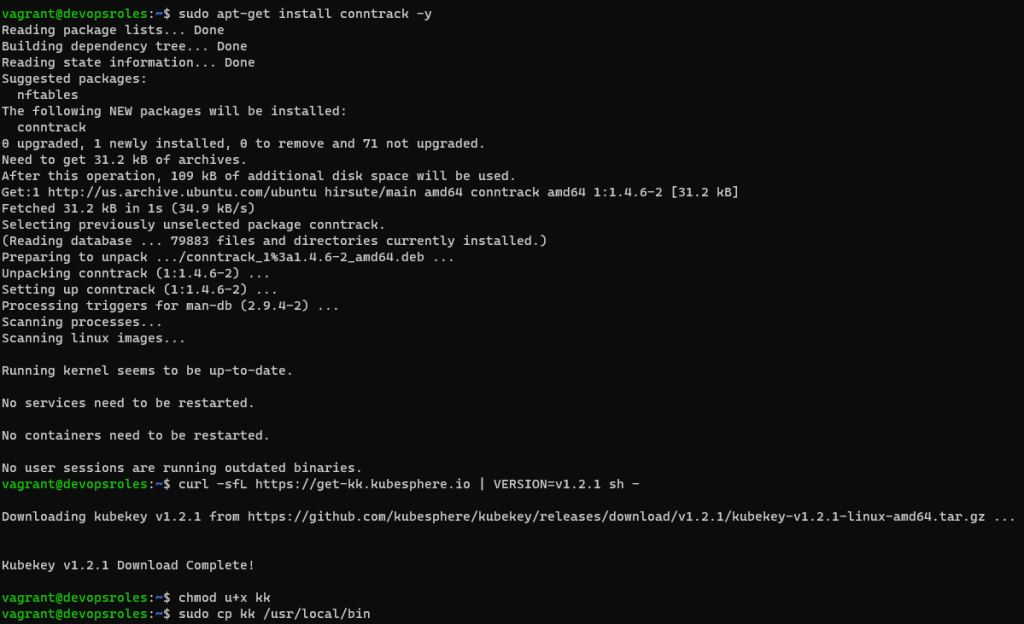
You need to download KubeKey and make it executable as the command below:
sudo apt-get install conntrack -y
curl -sfL https://get-kk.kubesphere.io | VERSION=v1.2.1 sh -
chmod u+x kkThe output terminal is the picture below:
Make the kk executable to run from any directory by copying the file to /user/local/bin directory with the command below:
sudo cp kk /usr/local/binVerify the install it
kk -hThe output terminal is as below:
vagrant@devopsroles:~$ kk -h
Deploy a Kubernetes or KubeSphere cluster efficiently, flexibly and easily. There are three scenarios to use KubeKey.
1. Install Kubernetes only
2. Install Kubernetes and KubeSphere together in one command
3. Install Kubernetes first, then deploy KubeSphere on it using https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer
Usage:
kk [command]
Available Commands:
add Add nodes to kubernetes cluster
certs cluster certs
completion Generate shell completion scripts
create Create a cluster or a cluster configuration file
delete Delete nodes or cluster
help Help about any command
init Initializes the installation environment
upgrade Upgrade your cluster smoothly to a newer version with this command
version print the client version information
Flags:
--debug Print detailed information (default true)
-h, --help help for kk
--in-cluster Running inside the cluster
Use "kk [command] --help" for more information about a command.Deploy the Cluster
You need to deploy the cluster with the command below:
sudo kk create clusterThis process will take some time.
The output terminal is as below:
vagrant@devopsroles:~$ sudo kk create cluster
+-------------+------+------+---------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+----------+------------+-------------+------------------+--------------+
| name | sudo | curl | openssl | ebtables | socat | ipset | conntrack | docker | nfs client | ceph client | glusterfs client | time |
+-------------+------+------+---------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+----------+------------+-------------+------------------+--------------+
| devopsroles | y | y | y | y | | | y | 20.10.12 | | | | UTC 14:06:10 |
+-------------+------+------+---------+----------+-------+-------+-----------+----------+------------+-------------+------------------+--------------+
This is a simple check of your environment.
Before installation, you should ensure that your machines meet all requirements specified at
https://github.com/kubesphere/kubekey#requirements-and-recommendations
Continue this installation? [yes/no]: yes
INFO[14:06:20 UTC] Downloading Installation Files
INFO[14:06:20 UTC] Downloading kubeadm ...
INFO[14:06:24 UTC] Downloading kubelet ...
INFO[14:06:32 UTC] Downloading kubectl ...
INFO[14:06:36 UTC] Downloading helm ...
INFO[14:06:38 UTC] Downloading kubecni ...
INFO[14:06:43 UTC] Downloading etcd ...
INFO[14:06:48 UTC] Downloading docker ...
INFO[14:06:52 UTC] Downloading crictl ...
INFO[14:06:55 UTC] Configuring operating system ...
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_local_reserved_ports = 30000-32767
vm.max_map_count = 262144
vm.swappiness = 1
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 524288
no crontab for root
INFO[14:06:56 UTC] Get cluster status
INFO[14:06:56 UTC] Installing Container Runtime ...
INFO[14:06:56 UTC] Start to download images on all nodes
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/pause:3.4.1
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/kube-apiserver:v1.21.5
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/kube-controller-manager:v1.21.5
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/kube-scheduler:v1.21.5
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/kube-proxy:v1.21.5
[devopsroles] Downloading image: coredns/coredns:1.8.0
[devopsroles] Downloading image: kubesphere/k8s-dns-node-cache:1.15.12
[devopsroles] Downloading image: calico/kube-controllers:v3.20.0
[devopsroles] Downloading image: calico/cni:v3.20.0
[devopsroles] Downloading image: calico/node:v3.20.0
[devopsroles] Downloading image: calico/pod2daemon-flexvol:v3.20.0
INFO[14:08:42 UTC] Getting etcd status
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
Configuration file will be created
INFO[14:08:42 UTC] Generating etcd certs
INFO[14:08:43 UTC] Synchronizing etcd certs
INFO[14:08:43 UTC] Creating etcd service
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/etcd-v3.4.13-linux-amd64.tar.gz to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/etcd-v3.4.13-linux-amd64.tar.gz Done
INFO[14:08:43 UTC] Starting etcd cluster
INFO[14:08:44 UTC] Refreshing etcd configuration
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/etcd.service → /etc/systemd/system/etcd.service.
INFO[14:08:47 UTC] Backup etcd data regularly
INFO[14:08:54 UTC] Installing kube binaries
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/kubeadm to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/kubeadm Done
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/kubelet to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/kubelet Done
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/kubectl to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/kubectl Done
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/helm to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/helm Done
Push /home/vagrant/kubekey/v1.21.5/amd64/cni-plugins-linux-amd64-v0.9.1.tgz to 10.0.2.15:/tmp/kubekey/cni-plugins-linux-amd64-v0.9.1.tgz Done
INFO[14:09:01 UTC] Initializing kubernetes cluster
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
W0323 14:09:02.442567 4631 utils.go:69] The recommended value for "clusterDNS" in "KubeletConfiguration" is: [10.233.0.10]; the provided value is: [169.254.25.10]
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.21.5
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[WARNING FileExisting-socat]: socat not found in system path
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [devopsroles devopsroles.cluster.local kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local lb.kubesphere.local localhost] and IPs [10.233.0.1 10.0.2.15 127.0.0.1]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] External etcd mode: Skipping etcd/ca certificate authority generation
[certs] External etcd mode: Skipping etcd/server certificate generation
[certs] External etcd mode: Skipping etcd/peer certificate generation
[certs] External etcd mode: Skipping etcd/healthcheck-client certificate generation
[certs] External etcd mode: Skipping apiserver-etcd-client certificate generation
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 7.502071 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.21" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node devopsroles as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/master(deprecated) node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node devopsroles as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: w6uaty.abpybmw8jhw1tdlg
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of control-plane nodes by copying certificate authorities
and service account keys on each node and then running the following as root:
kubeadm join lb.kubesphere.local:6443 --token w6uaty.abpybmw8jhw1tdlg \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:98d31447eb6457d74c0d13088aceed7ae8dd1fd0b8e98cb1a15683fcbb5ef4d5 \
--control-plane
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join lb.kubesphere.local:6443 --token w6uaty.abpybmw8jhw1tdlg \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:98d31447eb6457d74c0d13088aceed7ae8dd1fd0b8e98cb1a15683fcbb5ef4d5
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
node/devopsroles untainted
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
node/devopsroles labeled
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
service "kube-dns" deleted
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
service/coredns created
Warning: resource clusterroles/system:coredns is missing the kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration annotation which is required by kubectl apply. kubectl apply should only be used on resources created declaratively by either kubectl create --save-config or kubectl apply. The missing annotation will be patched automatically.
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:coredns configured
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
serviceaccount/nodelocaldns created
daemonset.apps/nodelocaldns created
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
configmap/nodelocaldns created
INFO[14:09:34 UTC] Get cluster status
INFO[14:09:35 UTC] Joining nodes to cluster
INFO[14:09:35 UTC] Deploying network plugin ...
[devopsroles 10.0.2.15] MSG:
configmap/calico-config created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created
daemonset.apps/calico-node created
serviceaccount/calico-node created
deployment.apps/calico-kube-controllers created
serviceaccount/calico-kube-controllers created
Warning: policy/v1beta1 PodDisruptionBudget is deprecated in v1.21+, unavailable in v1.25+; use policy/v1 PodDisruptionBudget
poddisruptionbudget.policy/calico-kube-controllers created
INFO[14:09:36 UTC] Congratulations! Installation is successful.To verify Kubectl has been installed with the command below:
kubectl --helpThe output terminal is as below:
vagrant@devopsroles:~$ kubectl --help
kubectl controls the Kubernetes cluster manager.
Find more information at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/
Basic Commands (Beginner):
create Create a resource from a file or from stdin.
expose Take a replication controller, service, deployment or pod and expose it as a new Kubernetes Service
run Run a particular image on the cluster
set Set specific features on objects
Basic Commands (Intermediate):
explain Documentation of resources
get Display one or many resources
edit Edit a resource on the server
delete Delete resources by filenames, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selector
Deploy Commands:
rollout Manage the rollout of a resource
scale Set a new size for a Deployment, ReplicaSet or Replication Controller
autoscale Auto-scale a Deployment, ReplicaSet, StatefulSet, or ReplicationController
Cluster Management Commands:
certificate Modify certificate resources.
cluster-info Display cluster info
top Display Resource (CPU/Memory) usage.
cordon Mark node as unschedulable
uncordon Mark node as schedulable
drain Drain node in preparation for maintenance
taint Update the taints on one or more nodes
Troubleshooting and Debugging Commands:
describe Show details of a specific resource or group of resources
logs Print the logs for a container in a pod
attach Attach to a running container
exec Execute a command in a container
port-forward Forward one or more local ports to a pod
proxy Run a proxy to the Kubernetes API server
cp Copy files and directories to and from containers.
auth Inspect authorization
debug Create debugging sessions for troubleshooting workloads and nodes
Advanced Commands:
diff Diff live version against would-be applied version
apply Apply a configuration to a resource by filename or stdin
patch Update field(s) of a resource
replace Replace a resource by filename or stdin
wait Experimental: Wait for a specific condition on one or many resources.
kustomize Build a kustomization target from a directory or URL.
Settings Commands:
label Update the labels on a resource
annotate Update the annotations on a resource
completion Output shell completion code for the specified shell (bash or zsh)
Other Commands:
api-resources Print the supported API resources on the server
api-versions Print the supported API versions on the server, in the form of "group/version"
config Modify kubeconfig files
plugin Provides utilities for interacting with plugins.
version Print the client and server version information
Usage:
kubectl [flags] [options]
Use "kubectl <command> --help" for more information about a given command.
Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).Deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard
Deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard with the command:
sudo kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml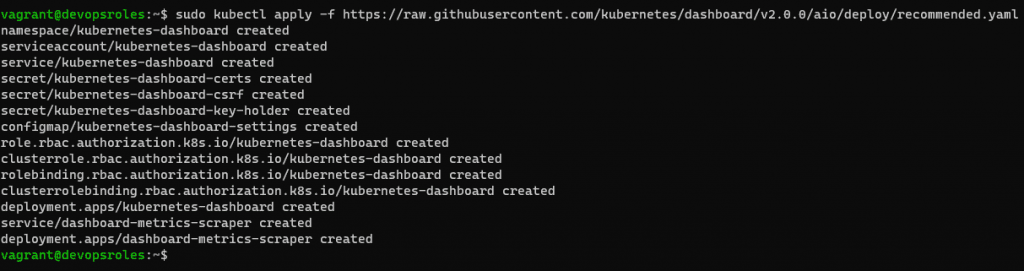
You need to deploy the dashboard, How to determine the IP address of the cluster uses the command below:
sudo kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboardThe output terminal is as below:
vagrant@devopsroles:~$ sudo kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.233.19.190 <none> 8000/TCP 64s
kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.233.23.203 <none> 443/TCP 64sYou might want to expose the dashboard via NodePort instead of ClusterIP
sudo kubectl edit svc kubernetes-dashboard -o yaml -n kubernetes-dashboardThis will open the configure file in vi editors.
Before:
type: ClusterIP
After change it
type: NodePort
Next, you must run the kubectl proxy command as below:
sudo kubectl proxyWhile the proxy is running, open a web browser and point it to the IP address and port number listed in the results from the sudo kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard command.
vagrant@devopsroles:~$ sudo kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.233.19.190 <none> 8000/TCP 47h
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.233.23.203 <none> 443:32469/TCP 47hOpen a web browser:
https://192.168.3.7:32469/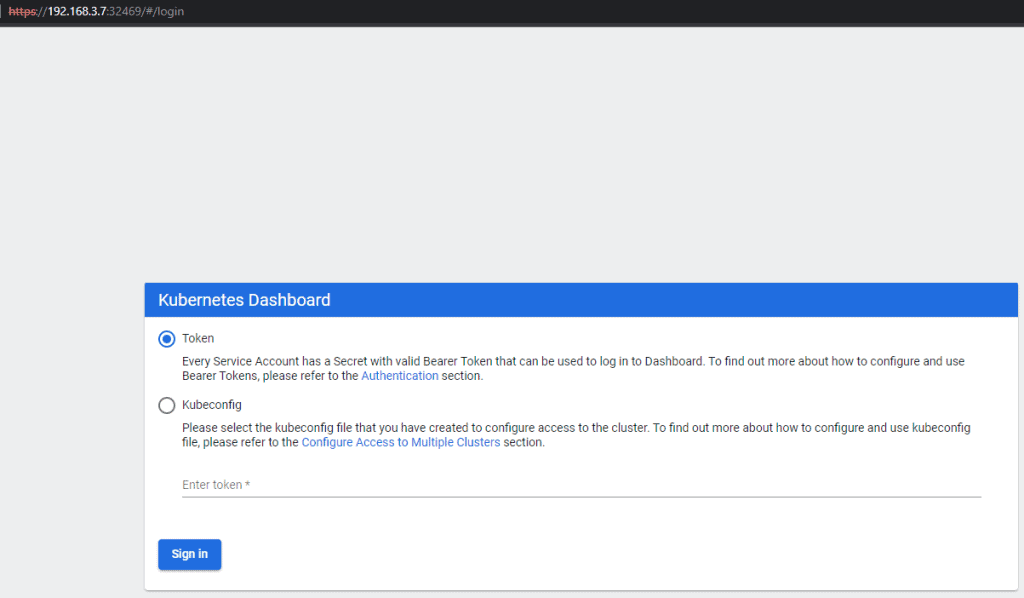
To log in to the dashboard. You need to create a ServiceAccount object and a ClusterRoleBinding object. Create the account with the name admin-user in the namespace kubernetes-dashboard
cat <<EOF | sudo kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
EOFCreate a ClusterRoleBinding object.
cat <<EOF | sudo kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
EOFTo retrieve that token with the command below:
sudo kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe secret $(kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get secret | grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')Expected output:
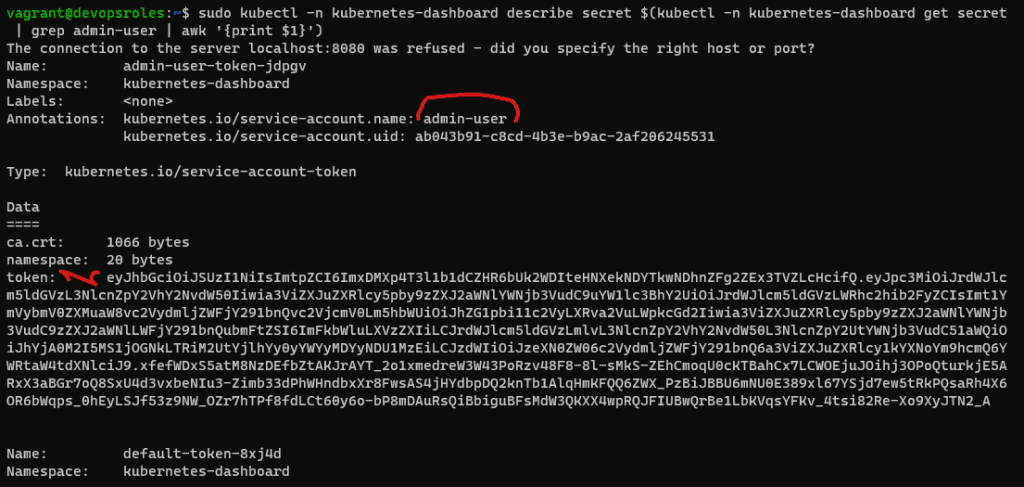
The result,
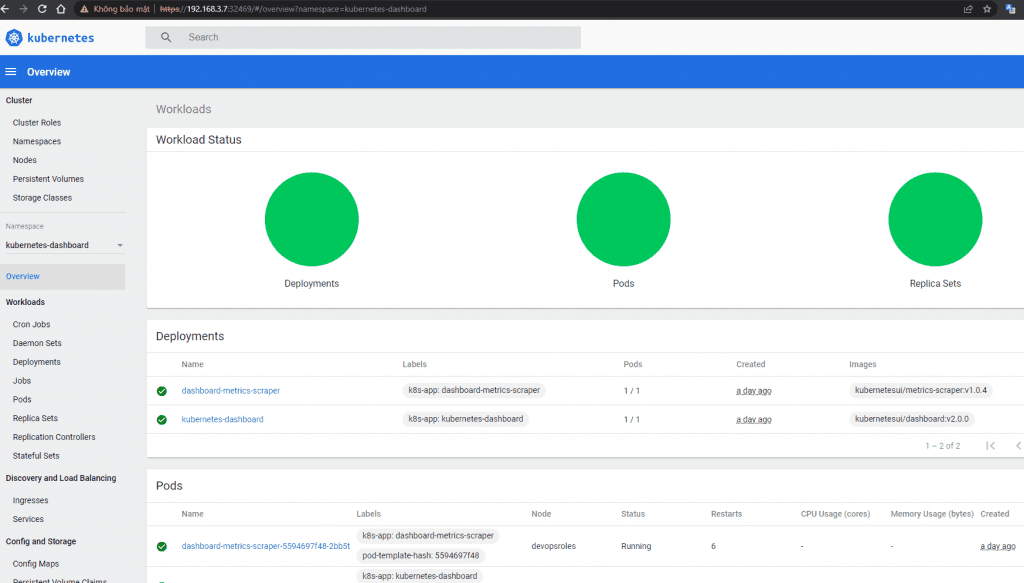
This isn’t production-ready, but it’s a great way to get up to speed with Kubernetes and even develop for the platform.
The result is Docker Kubernetes containers running Ubuntu Server. Install Kubernetes Cluster with KubeKey
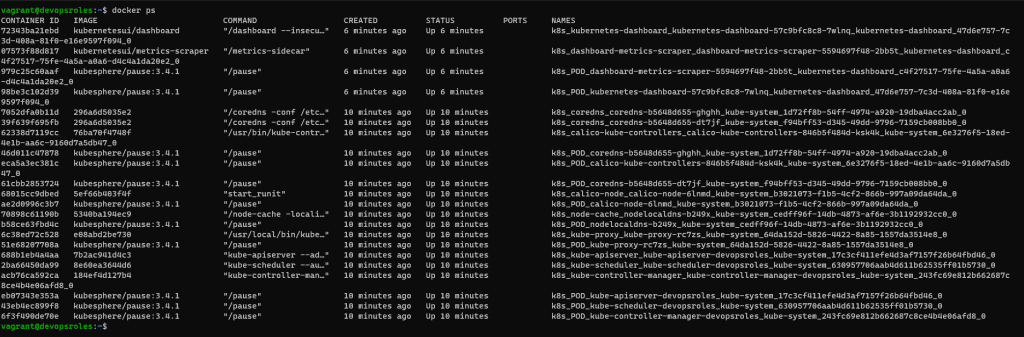
Conclusions
You have to Install Kubernetes Cluster with KubeKey. I hope will this your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

