Table of Contents
Introduction
In this tutorial, How to run Python on Docker. Python is a programming language. Python Docker image is the latest point release.
The Docker image version was released in March 2022.
Image 3.9 release
Debian 11 3.9.2
Ubuntu 20.04 3.9.5
RHEL 8 3.9.7
RHEL 9 3.9.10
Docker python 3.9.14
You need to install Docker on Ubuntu.
The working directory python docker:
root@devopsroles:~/dockerpython# ls -lF
total 20
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 111 Nov 20 14:31 app.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 236 Nov 20 15:00 Dockerfile
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 20 Nov 20 14:27 requirements.txtHow to build a Docker container running a simple Python application.
Setup dockerfile python
Create a folder and create a virtual environment. This isolated the environment for the Python Docker project.
For example
mkdir dockerpython
cd dockerpython
python3 -m venv dockerpython
source dockerpython/bin/activate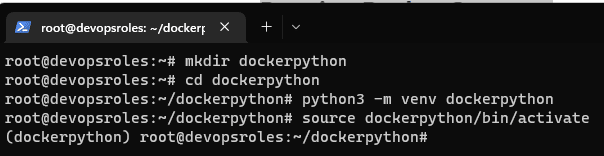
Create a new file dockerfile python.
FROM python:3.9-slim-buster
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
EXPOSE 5000
CMD [ "python3", "-m" , "flask", "run", "--host=0.0.0.0", "--port=5000"]Save and close.
Create the Python App
Create an app.py file. For example as below
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello, Docker!'Save and close.
Create the requirements.txt file. This contains dependencies for the app to run.
For example, we add the packages for the requirements.txt file.
Flask=2.0.3
pylintOr method 2: show all packages installed via pip use pip3 freeze and save to the requirements.txt file.
pip3 install Flask
pip3 freeze | grep Flask >> requirements.txtwe will test if the works localhost using the command below
python3 -m flask run --host=0.0.0.0 --port=5000Open the browser with the URL http://localhost:5000
Docker Build image and container
You build a Docker image from created Dockerfile. Use the command below to build the Docker image
docker build --tag dockerpython .Tag the image using the syntax
docker tag <imageId> <hostname>/<imagename>:<tag>For example, Tag the image.
docker tag 8fbb6cdc5e76 huupv/dockerpython:latest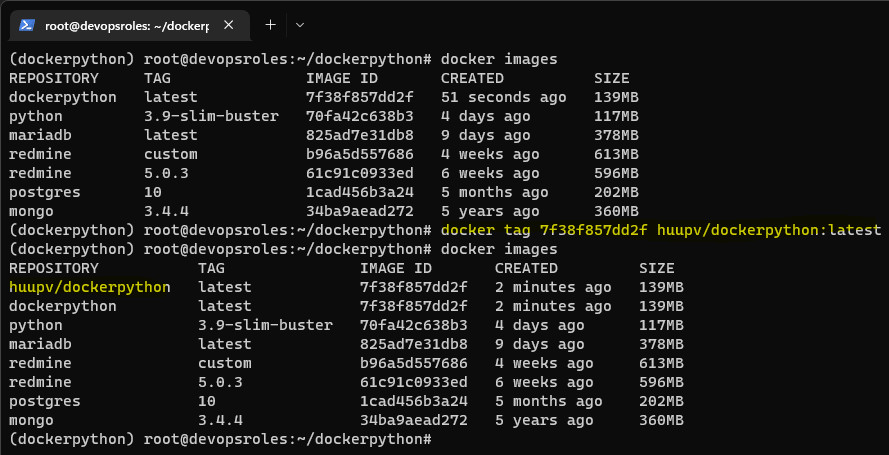
Now, the Run Docker image has the created and tagged with the command line below:
docker run --publish 5000:5000 <imagename>Use the command below to list containers running.
docker psThe result below:
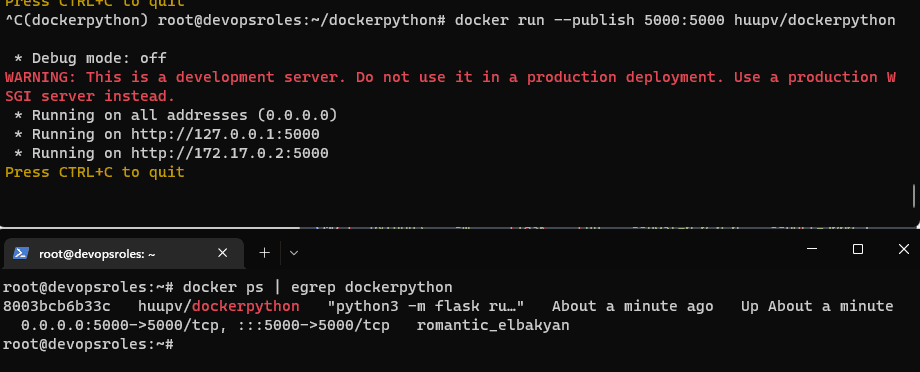
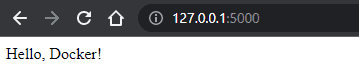
You can now test your application using http://localhost:5000 on your browser.
Docker pushed and retrieved from Docker Hub
The container will be pushed and retrieved from the Docker Hub registry. The command simple
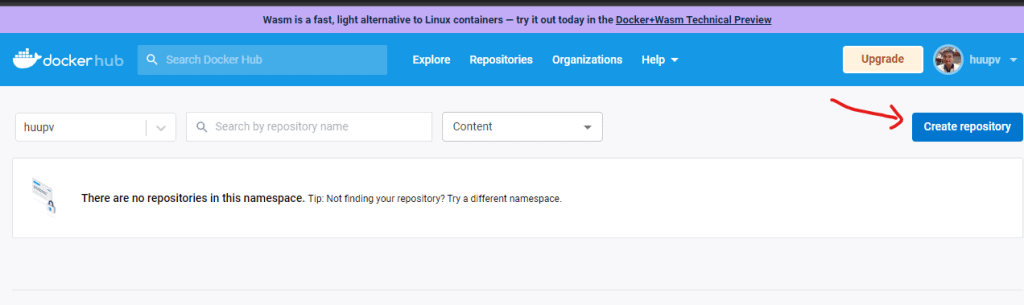
docker push <hub-user>/<repo-name>:<tag>.On the website Docker Hub. Click Create Repository to give the repo a name.
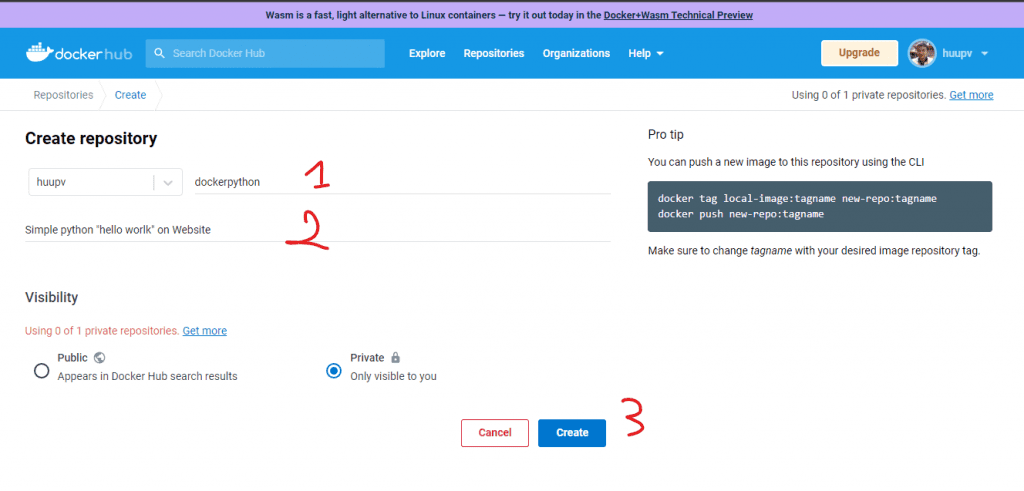
Create 1 repo name and description as below:
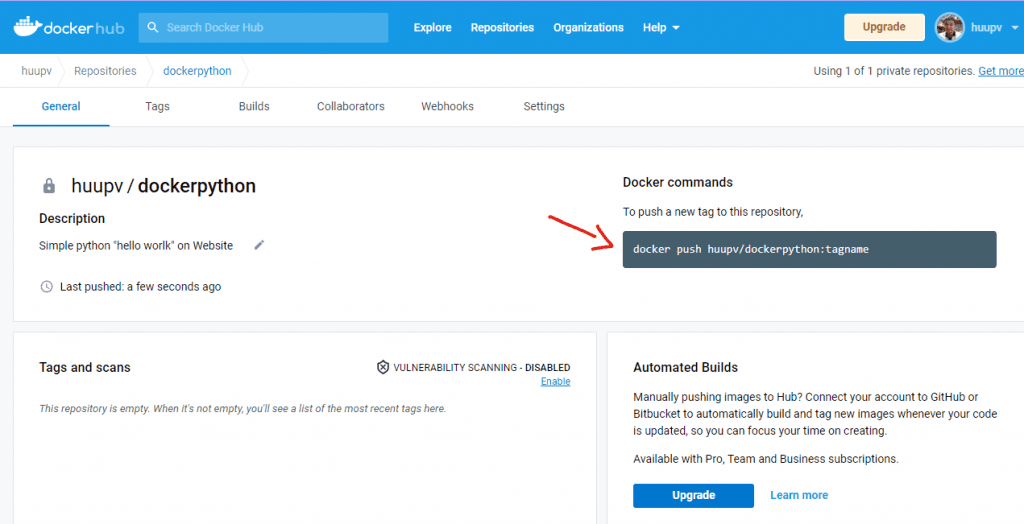
Copy the command to your terminal, replacing tagname with version latest.
In your terminal, we run the command docker login to connect the remote repository to the local environment. Add username and password to valid login.
Run the command to push to the repository you created it.
docker push <hub-user>/<repo-name>:tagname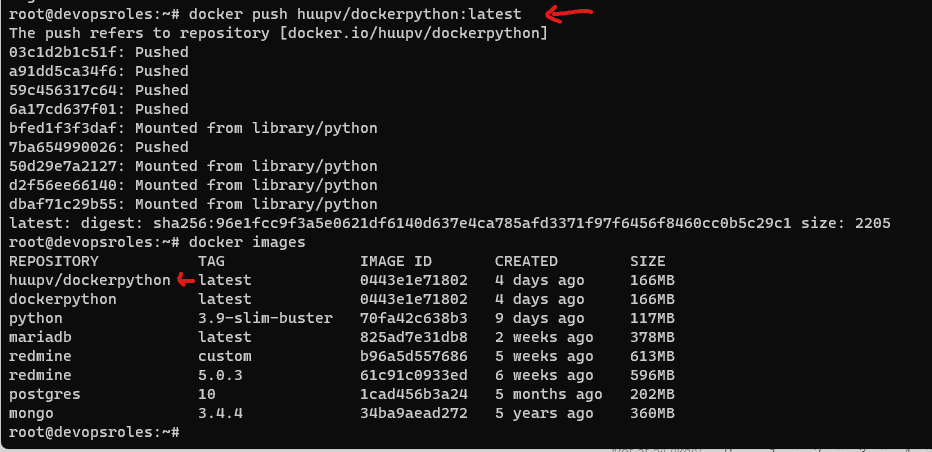
Confirm your image to be pushed to the Docker Hub page
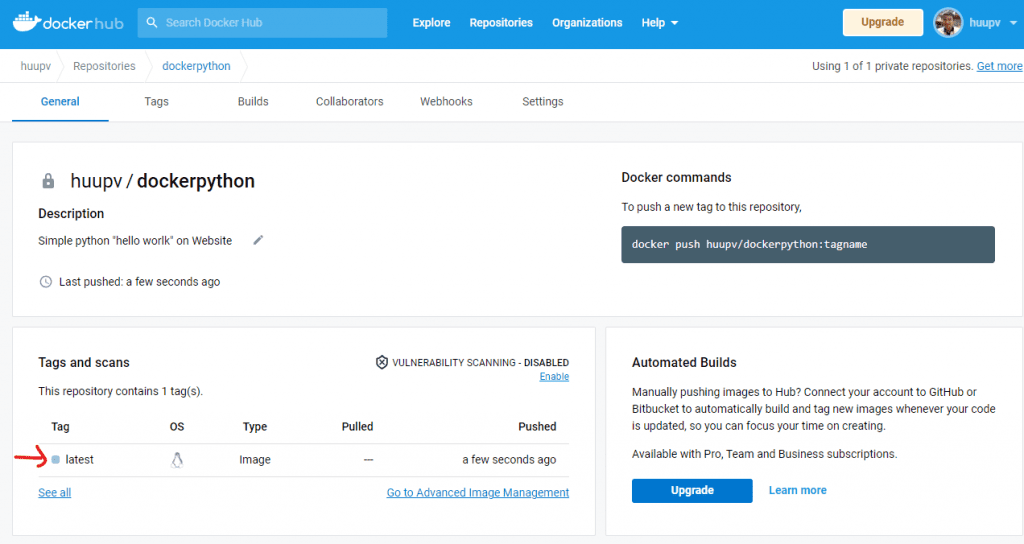
In any terminal, Docker pulls the Docker image from Docker Hub.
root@devopsroles:~# docker pull huupv/dockerpython:latestFor example, use Docker Compose
version: "3.9"
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
volumes:
- .:/app
- logvol:/var/log
links:
- redis
redis:
image: redis
volumes:
logvol: {}Conclusion
You know How to run Python on Docker. I hope this will be helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

