Table of Contents
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved to become a cornerstone of modern technology, particularly through AI agents. These intelligent systems are designed to perform tasks automatically, make informed decisions, and adapt to complex environments. The rise of AI agents has reshaped industries ranging from customer service to finance, providing businesses with the ability to automate processes, optimize operations, and improve overall efficiency.
In this article, we will explore what AI agents are, how they work, their applications, and provide real-world examples of their use. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of AI agents and how they can benefit various sectors.
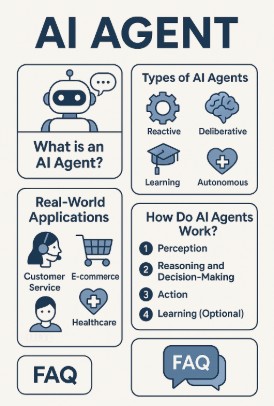
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a system that performs tasks or solves problems by autonomously perceiving its environment, reasoning based on this data, and acting according to its findings. These agents are designed to operate without continuous human intervention, making them invaluable in industries where tasks need to be executed repeatedly or under time constraints.
AI agents come in various types, such as reactive, deliberative, learning-based, and autonomous agents, each tailored to different use cases and requirements.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
- Autonomy: AI agents can make decisions without human input, based on predefined rules or machine learning models.
- Adaptability: They can learn from past actions and improve their performance over time.
- Interactivity: AI agents can interact with both the environment and users, responding to changes in real-time.
- Goal-Oriented: They work towards specific objectives or tasks, often optimizing for the best outcome.
Types of AI Agents
There are several types of AI agents, each suited to different tasks and levels of complexity. Understanding these types is key to determining which AI agent is best for your needs.
1. Reactive Agents
Reactive agents are the simplest form of AI agents. They respond to stimuli from their environment based on predefined rules or conditions, with no internal state or memory.
- Example: A thermostat in a smart home adjusts the temperature based on the room’s current conditions, without retaining information from past adjustments.
2. Deliberative Agents
These agents are capable of reasoning and planning. They take into account multiple factors before making decisions and can adapt their strategies based on new information.
- Example: An AI-driven personal assistant, like Google Assistant, that not only responds to commands but also plans daily schedules and adapts to user preferences over time.
3. Learning Agents
Learning agents are designed to improve their performance over time by learning from experiences. This learning typically occurs through methods like reinforcement learning, where the agent receives feedback based on its actions.
- Example: Self-driving cars, which learn how to drive more safely and efficiently through trial and error, constantly improving from past experiences.
4. Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents can operate independently, often in complex, unpredictable environments. They do not require constant human oversight and can perform long-term tasks autonomously.
- Example: Autonomous drones used for agricultural monitoring, which fly across fields to collect data and make decisions about crop management without human intervention.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are increasingly being integrated across various industries, where they help automate processes, make decisions, and enhance user experiences. Let’s explore some real-world applications of AI agents.
1. AI Agents in Customer Service
AI-powered customer service agents, such as chatbots, are transforming how businesses interact with customers. These agents can handle customer inquiries, troubleshoot problems, and provide assistance without human involvement.
- Example: Zendesk’s Answer Bot is a conversational AI agent that helps businesses automate customer support, providing instant answers to common questions and redirecting complex inquiries to human agents.
2. AI Agents in E-commerce
In e-commerce, AI agents can analyze consumer behavior, recommend products, and optimize inventory management. These agents enable a more personalized shopping experience, improving sales and customer satisfaction.
- Example: Amazon’s recommendation engine is an AI agent that suggests products based on users’ previous searches, purchases, and preferences, driving higher conversion rates.
3. AI Agents in Healthcare
AI agents are making strides in healthcare, particularly in diagnostics, personalized medicine, and patient care. These agents can process large amounts of medical data to assist healthcare professionals in decision-making.
- Example: IBM Watson Health is an AI system that can analyze patient data and medical literature to provide treatment recommendations and identify potential risks.
4. AI Agents in Finance
In finance, AI agents are used for risk assessment, fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and customer service. These agents can process vast amounts of data and make decisions in real-time, often faster and more accurately than humans.
- Example: Robo-advisors like Betterment use AI agents to provide automated financial planning and investment management based on individual user goals and risk tolerance.
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents typically consist of several key components that enable them to perform tasks autonomously. These components include:
1. Perception
Perception involves collecting data from the environment, such as images, sounds, or sensor readings. AI agents use various input sources, such as cameras, microphones, or APIs, to perceive the world around them.
- Example: A smart home AI agent uses sensors to detect temperature, humidity, and motion, adjusting the home’s environment accordingly.
2. Reasoning and Decision-Making
Once an AI agent perceives its environment, it processes this data to make decisions. This stage involves the application of algorithms, machine learning models, or rules to determine the best course of action.
- Example: A self-driving car analyzes its surroundings to decide whether to stop, accelerate, or turn, based on factors like traffic signals and pedestrian movement.
3. Action
After reasoning, the AI agent takes action. This could involve sending a command to another system, displaying a response to the user, or physically performing a task, depending on the agent’s purpose.
- Example: An AI-powered robot arm in a manufacturing plant picking up objects and placing them on a conveyor belt.
4. Learning (Optional)
Learning agents go a step further by incorporating feedback from their actions to refine future decision-making. These agents use machine learning techniques to adapt over time, improving their accuracy and efficiency.
- Example: A recommendation system that gets better at suggesting content based on users’ interactions with previous suggestions.
Examples of AI Agents in Action
Let’s walk through some practical scenarios that demonstrate how AI agents operate:
Basic Example: AI Chatbots in Customer Support
Imagine a customer interacts with a chatbot on a retail website. The chatbot, an AI agent, analyzes the customer’s query and provides an instant response, such as guiding them to the appropriate product or solving a common issue.
- Process:
- Perception: The chatbot receives input (text) from the user.
- Reasoning: It interprets the query using natural language processing (NLP) algorithms.
- Action: It provides a relevant response or action (such as guiding the user to a product page).
- Learning: Over time, the chatbot improves its responses based on customer interactions and feedback.
Advanced Example: Self-Driving Car
A self-driving car is a highly complex AI agent that needs to process massive amounts of real-time data to navigate safely. The car uses sensors, cameras, and radar to perceive its environment and make decisions about acceleration, braking, and steering.
- Process:
- Perception: The car detects nearby vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signals, and road conditions.
- Reasoning: The car evaluates the best route, considers obstacles, and adjusts speed.
- Action: It steers, accelerates, or brakes accordingly.
- Learning: The car improves its decision-making over time through reinforcement learning and real-world driving experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about AI Agents
1. What is the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
An AI agent is a broader concept that refers to any AI-driven system capable of acting autonomously to achieve goals. A chatbot is a specific type of AI agent designed for conversational interaction, often used in customer service.
2. Are AI agents capable of learning from mistakes?
Yes, some AI agents, especially learning agents, can learn from their mistakes by adjusting their behavior based on feedback, using techniques such as reinforcement learning.
3. Can AI agents replace humans in all tasks?
AI agents are highly effective at automating repetitive and rule-based tasks. However, tasks that require deep human empathy, creativity, or complex reasoning beyond current AI capabilities are still better handled by humans.
4. What industries benefit the most from AI agents?
AI agents are used across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, customer service, automotive, and manufacturing. Industries that require repetitive tasks or data analysis stand to benefit the most.
Conclusion
AI agents are revolutionizing the way businesses and individuals interact with technology. From basic chatbots to advanced autonomous systems, AI agents offer solutions that improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and create new opportunities. Understanding how these agents work and their real-world applications can help organizations leverage AI to stay ahead of the curve.
Whether you’re exploring AI for customer service, e-commerce, or healthcare, the future of AI agents promises even more sophisticated and impactful solutions across all industries.
For more information about AI and its applications, check out IBM Watson and Google AI.Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!
